- 1. Writing: The Birth of Recorded Knowledge
- 2. The Alphabet: Simplifying the Written Word
- 3. Papyrus and Paper: Making Knowledge Portable
- 4. The Library: Organizing the World’s Knowledge
- 5. The Academy: Institutions for Higher Learning
- 6. Numerals and Zero: The Language of Mathematics
- 7. The Abacus: An Early Calculator
- 8. Maps and Globes: Visualizing our World
- 9. Mentorship: Learning from the Wise
- 10. The Value of Debate and Inquiry
- A Legacy of Learning
- Why Should You Care?
- Key Takeaways
- Keywords
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Myth Buster
- Let’s Talk
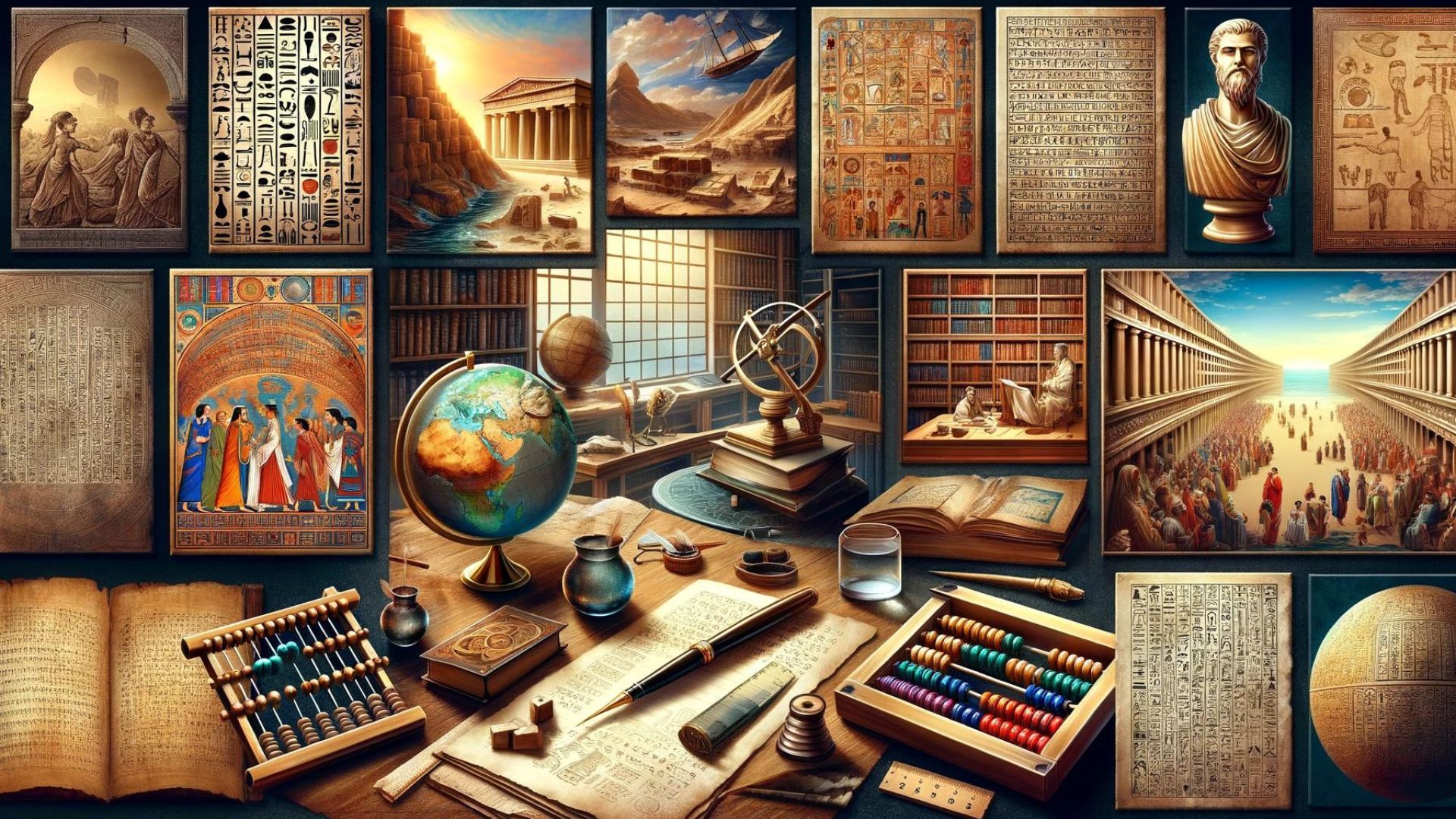
History is often viewed through the lens of grand empires, wars, and monumental architecture. But amidst these narratives lies another incredible story: the evolution of education and learning. From the dawn of civilization, brilliant minds paved the way for how we share knowledge, developing innovations that still shape our world today.
Let’s travel back in time and explore the top 10 ancient educational inventions that changed everything:
1. Writing: The Birth of Recorded Knowledge
Imagine a world where ideas and stories lived only in spoken words, disappearing as quickly as they were uttered. That changed with the invention of writing. From the cuneiform script of Mesopotamia to the hieroglyphs of Egypt, humans could suddenly record history, laws, literature, and scientific observations for future generations. It became the foundation of structured learning.
Real-life connection: Think of the power writing gives you! It allows you to create shopping lists, take notes, capture your dreams in a journal, or even compose heartfelt letters.
2. The Alphabet: Simplifying the Written Word
Early writing systems were complex, with hundreds or even thousands of symbols to master. The alphabet revolutionized literacy. Phoenicians developed a system with just a few dozen characters representing sounds, making writing far easier to learn. This paved the way for widespread education and knowledge sharing.
Real-life connection: Every time you read a book, text a friend, or write down a recipe, you’re using the power of the alphabet!
3. Papyrus and Paper: Making Knowledge Portable
Clay tablets were heavy and cumbersome. With the invention of papyrus in Egypt and later paper in China, knowledge became portable. Scrolls and books could be easily transported and shared, fostering the spread of ideas across vast distances.
Real-life connection: Imagine the world without notebooks, textbooks, or even magazines! Papyrus and paper made organized learning and the sharing of discoveries possible.
4. The Library: Organizing the World’s Knowledge
The legendary Library of Alexandria was an ancient wonder, housing vast collections of scrolls and attracting scholars from across the known world. Libraries became centers of learning not just storage spaces – they organized and preserved humanity’s collective knowledge.
Real-life connection: Libraries remain cornerstones of education, offering access to countless resources. Think of all you can learn just by exploring the shelves of your local library!
5. The Academy: Institutions for Higher Learning
Plato’s Academy in Athens marked the birth of formal higher education. Here, scholars gathered to debate philosophy, mathematics, and the sciences, advancing knowledge systematically. This model inspired universities that continue to drive innovation and critical thinking today.
Real-life connection: Colleges and universities still uphold this tradition of focused learning. If you pursue higher education, you’ll be part of a legacy stretching back to ancient Greece!
6. Numerals and Zero: The Language of Mathematics
The Hindu-Arabic numeral system, including the revolutionary concept of zero, transformed how we understand and manipulate numbers. Ancient Indian mathematicians laid the groundwork for advances in science, engineering, and commerce.
Real-life connection: Imagine trying to do complex calculations with Roman numerals! Modern mathematics, vital for so many fields, owes a debt to these ancient thinkers.
7. The Abacus: An Early Calculator
While simple by today’s standards, the abacus was a groundbreaking tool for performing mathematical operations. Its use, originating in ancient Mesopotamia, promoted numeracy and problem-solving skills.
Real-life connection: Though we have powerful calculators now, the principle of the abacus helps us visualize mathematical concepts.
8. Maps and Globes: Visualizing our World
Early maps and globes allowed civilizations to grasp their place in the world, navigate oceans, and plan trade routes. They also sparked curiosity about distant lands and cultures, broadening perspectives.
Real-life connection: Next time you use a map app or study geography, remember the ancient cartographers who first charted our planet.
9. Mentorship: Learning from the Wise
In many ancient cultures, apprenticeship and mentorship were vital to passing down skills and knowledge. Young learners would observe and work alongside experienced masters, gaining practical and life wisdom.
Real-life connection: The value of mentorship persists – whether seeking career guidance, honing a skill, or learning from those with more experience, we continue to benefit from this personalized approach to learning.
10. The Value of Debate and Inquiry
Socrates, the famous Athenian philosopher, didn’t just provide answers – he asked questions. This technique, the Socratic Method, encouraged critical thinking, logical reasoning, and the pursuit of deeper truth.
Real-life connection: When you encounter conflicting information or have to make a decision, channel your inner Socrates! Ask probing questions, consider various perspectives, and seek evidence-based reasoning.
A Legacy of Learning
This exploration reveals that the quest for knowledge is a timeless, unifying force throughout human history. Their ingenuity echoes across millennia, shaping our educational practices and fueling our thirst for understanding.
Action Point: Let these ancient innovations inspire your own learning! Embrace curiosity, seek reliable sources, engage in respectful debate, and never stop questioning the world around you.
Why Should You Care?
- Appreciation for the past: Understanding ancient educational innovations gives us a deeper appreciation for the long and arduous journey of knowledge acquisition and preservation.
- Inspiration for the present: These ancient breakthroughs highlight the enduring principles of effective learning: curiosity, critical thinking, organized knowledge, and accessibility. We can adapt and build upon these principles in our own educational systems.
- Global perspective: Learning about diverse cultures’ contributions to education broadens our understanding of how societies transmit values and skills across generations.
Key Takeaways
- Knowledge preservation: Writing systems were essential for recording and transmitting knowledge beyond the limits of spoken language.
- Accessibility and literacy: The alphabet, papyrus, and paper made sharing knowledge easier and promoted widespread literacy.
- Centers of knowledge: Libraries and academies were hubs of intellectual pursuits, fostering discovery and innovation.
- Tools for thinking: Numerals, zero, and the abacus revolutionized mathematical thinking, paving the way for scientific and technological progress.
- Mentoring and debate: Personalized guidance and the questioning of ideas remain cornerstones of effective learning.
Keywords
- Writing systems: Systems of symbols used to represent spoken language (cuneiform, hieroglyphs).
- Alphabet: A set of letters representing individual sounds, simplifying writing and reading.
- Papyrus/Paper: Early writing materials that made knowledge portable.
- Library: An organized collection of books and resources for research and learning.
- Academy: An institution for higher learning and scholarly debate.
- Numerals: Symbols used to represent numbers.
- Zero: The concept and symbol ‘0’, a revolutionary mathematical breakthrough.
- Abacus: A simple calculating tool using beads and rods.
- Mentorship: Guidance and knowledge transfer from an experienced person to a learner.
- Socratic Method: Learning through questioning, dialogue, and critical reasoning.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Were there schools in ancient times? Yes, various forms existed – from temple schools in Mesopotamia to philosophical academies in Greece, and schools for the elite in Rome.
- Who had access to education in the ancient world? It largely depended on social class, gender, and location. The wealthy and privileged had better access, but there were efforts to provide some public education in certain cultures.
- What subjects were taught? Reading, writing, arithmetic, religion, literature, music, and sometimes physical training. Specialized academies focused on philosophy, law, or medicine.
Myth Buster
- Myth: Ancient people were less intelligent than us.
- Reality: Ancient cultures possessed brilliant minds that developed complex systems, made scientific discoveries, and created timeless works of art and literature. Their innovations laid the foundation for much of our knowledge.
Let’s Talk
- Do you think modern education sufficiently emphasizes critical thinking? Why or why not?
- How can we make learning more accessible and engaging for everyone today?
- Which ancient innovation do you find most impactful, and why?
Share your thoughts in the comments below!









0 Comments