- Episode Preview
- Introduction
- The Building Blocks of Memory
- The Power of Emotion and Narrative in Learning
- Memory Techniques & Strategies
- Practical Application & Case Study – From Classroom to Career
- Practical Application & Case Study – Digital Tools & the Future of Learning
- Let’s Learn Vocabulary in Context
- Let’s Discuss & Write
- Outro
Episode Preview
Introduction
Imagine a cold, rainy evening when Emily, a determined college student, was drowning in a sea of lecture notes and exam dates. Frustrated by forgotten details and mounting stress, she stumbled upon an old, dusty journal in her attic—a journal filled with stories from her grandmother about secret family techniques for remembering important events. Intrigued, Emily discovered that these weren’t just quirky anecdotes; they were early hints at the science behind memory and learning retention. That night, everything changed for her: she realized that our brains are wired not just to store facts, but to remember the emotions and stories behind them.
In today’s episode, we’ll unravel the mystery of how our memories are formed and explore powerful techniques that turn everyday learning into memorable experiences. We’re asking: How does our brain decide what to keep and what to forget? What makes some lessons stick for a lifetime while others fade away? And how can we harness this knowledge to supercharge our learning and language skills?
Here’s a sneak peek at what we’ll cover:
- The Building Blocks of Memory: We’ll dive into how memories are created, stored, and retrieved—think of it as the architecture behind your brain’s filing system.
- The Power of Emotion and Narrative in Learning: Discover why emotionally charged stories aren’t just entertaining—they’re essential for making memories stick.
- Memory Techniques & Strategies: Learn about mnemonics, the method of loci, and other clever tricks that can transform your study habits.
- Practical Application & Case Study – From Classroom to Career: Hear a real-life success story of someone who applied these techniques to overcome academic and professional hurdles.
- Practical Application & Case Study – Digital Tools & the Future of Learning: Explore how modern technology and AI are revolutionizing the way we enhance memory and retention.
And that’s not all! After these five sections, we’ll move into our signature Learn Vocabulary in Context segment—where we’ll break down key terms from today’s discussion—and wrap up with Discussion Questions to spark your own exploration and application of these memory-boosting insights.
So, if you’ve ever wondered why some lessons linger in your mind while others vanish, or if you’re ready to transform your learning experience through the magic of storytelling and science, stick around. Let’s dive into the science of memory and unlock the secrets to lifelong learning together!
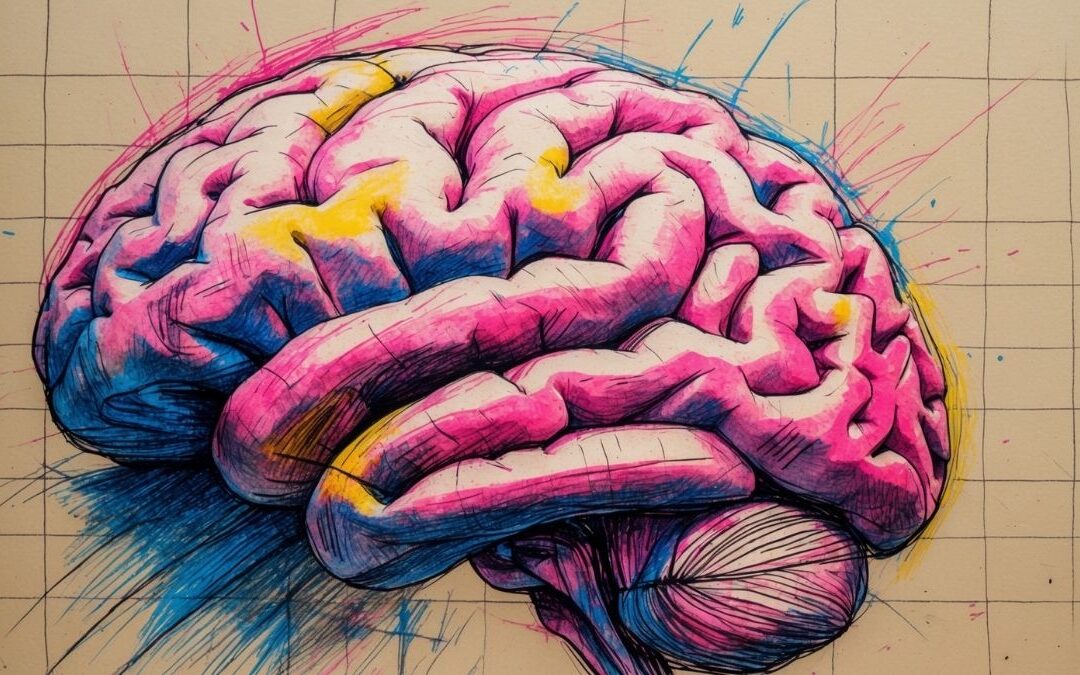
The Building Blocks of Memory
Welcome back, everyone! In this segment, we’re going to dive deep into the very foundation of what makes our minds tick—the building blocks of memory. Now, before we get started, I have a little question for you: if you had to choose just one part of the memory process that’s absolutely key to forming lasting memories, which would it be—encoding, storage, or retrieval? Hold onto that thought, and we’ll come back to it by the end of our discussion.
Let’s start by imagining your brain as the world’s most intricate, high-tech library. In this library, every experience, every piece of information, is like a book waiting to be shelved. But before any of these books can be placed on the shelf, they first have to be written. That “writing” process in our brain is what scientists call encoding.
Encoding is the moment when your brain takes in information—whether it’s a conversation you’re having, the sight of a beautiful sunset, or even a word in a new language—and transforms it into a format that it can store later. Think of it like snapping a photograph: the camera (your brain) captures an image of what’s in front of it, but if you’re not paying attention, that photo might turn out blurry or off-center. When you’re actively engaged—when your emotions are stirred or your curiosity is piqued—the picture becomes crisp, detailed, and more likely to be saved for future viewing.
Now, imagine that crisp photograph being handed off to a skilled librarian whose job is to organize these memories. This is where storage comes into play. Storage is the process by which your brain categorizes and files these encoded memories away, sometimes in an orderly filing system, and sometimes in a more haphazard way that can make finding them later a bit of a challenge. Our brains have multiple “shelves” for different kinds of information: one for short-term memories that might last just seconds or minutes, and another for long-term memories that can last a lifetime. There’s also what we call working memory, which is like the librarian’s desk where things are temporarily held before they’re either discarded or sent off to long-term storage.
But what happens when you need to recall a memory—a friend’s birthday, a fact for an exam, or even the plot of your favorite movie? That’s where retrieval comes into the picture. Retrieval is like searching for that exact book in the vast library of your brain. It’s the process that allows you to access stored information. Sometimes retrieval is smooth and effortless, much like finding a bestseller on the library’s display shelf. Other times, it’s like searching for a needle in a haystack, especially if the memory isn’t well encoded or has been buried under other similar memories.
Now, let’s make this a bit interactive. As you listen, take a moment to reflect on a time when you couldn’t quite remember something important—a name, a piece of trivia, or even a lesson you’d studied. Ask yourself: Was it that you didn’t pay enough attention when you first learned it, meaning the encoding was off? Or did you simply misplace it on the shelves of your mind, indicating a storage issue? Or perhaps you had all the information tucked away neatly, but for some reason, you just couldn’t access it when needed—could that be a retrieval problem? Keep those thoughts in mind as we explore each of these stages in more detail.
Let’s circle back to encoding. This initial phase is crucial because it sets the stage for everything that follows. When we encode information, our brain isn’t just passively recording data. It’s actively interpreting it, influenced by our senses, emotions, and even the context in which we experience it. For example, think about the last time you learned a new word in English. Perhaps you heard it used in a funny, relatable story or connected it with a vivid image in your mind. That kind of active engagement makes the encoded information far more robust. Studies have shown that the more meaning you can attach to a piece of information, the stronger the memory trace becomes.
Moving on to storage, this is where your brain’s architecture really shows off its complexity. The brain doesn’t store memories in one neat, tidy location. Instead, different parts of the brain specialize in storing different kinds of information. The hippocampus, a seahorse-shaped structure deep within your brain, plays a key role in converting short-term memories into long-term ones. Meanwhile, other areas of the brain help store sensory details like sights, sounds, and even smells. The fascinating part is that these memories aren’t stored in isolation—they’re interconnected, forming networks that can be activated by a single cue. This interconnectedness is why one memory can trigger another, sometimes unexpectedly.
Now, let’s talk about retrieval. Retrieval is not just a passive process where you pull up a file from a shelf; it’s an active reconstruction of your past experiences. Every time you recall a memory, you’re not just replaying a perfect recording. Instead, you’re piecing together details from various parts of your brain, and this reconstruction can sometimes change the memory itself. That’s why you might notice that your recollection of an event can differ slightly from one day to the next. It’s a bit like retelling a favorite story—each telling might add a new twist or emphasize different details, but the core of the memory remains intact.
An interesting aspect of retrieval is the role of cues. These are signals or triggers—like a familiar scent, a particular place, or even a specific emotion—that help your brain locate the memory you’re trying to recall. Imagine walking into a room that reminds you of your childhood; suddenly, memories flood back. That’s your brain using cues to retrieve stored information. It’s a dynamic process, and one that highlights how our memories are intertwined with our sensory experiences and emotional states.
Let’s make this even more interactive. I’d love for you to try a little exercise. Think of a simple word—say, “tree.” Now, close your eyes for a moment and picture a tree. What details come to mind? Perhaps the rough texture of the bark, the way the leaves rustle in the wind, or the shadow it casts on a sunny day. In that brief moment, you’ve encoded an image, stored it in your mind, and now you’re retrieving it to visualize it. It might seem simple, but this little exercise encapsulates the entire memory process in a way that’s personal and immediate.
So, let’s tie it all together. We started by exploring encoding—our brain’s way of taking in and transforming experiences into lasting impressions. We moved on to storage, the complex process of organizing and filing those impressions away, sometimes in surprising and intricate ways. Finally, we delved into retrieval, the art of pulling those memories back into our conscious mind, often with the help of cues and context.
Now, let’s return to that question I asked at the very beginning: If you had to choose one part of the memory process that’s most critical for forming lasting memories, which would it be—encoding, storage, or retrieval? The answer isn’t as simple as picking one over the others, because they all work together in a beautiful, interconnected dance. However, if we had to shine a spotlight on one, many scientists would argue that encoding is the foundational step. Without a strong, clear encoding process, even the most efficient storage and retrieval systems can’t compensate. In other words, the quality of the memory starts right at the moment you experience it.
So, if you want your memories to be long-lasting, it all begins with paying attention and engaging deeply with what you’re learning. That’s why techniques like linking new information to stories, emotions, or vivid images are so effective—they help to ensure that the encoding process is as robust as possible, setting the stage for successful storage and retrieval later on.
As we wrap up this section, I invite you to think about your own experiences. Reflect on a time when you were deeply engaged in learning something new, and consider how that engagement helped cement the information in your mind. And remember that key question: which part of the process is most critical? While we’ve revealed that encoding is often the linchpin, don’t forget that without proper storage and retrieval, even the best encoding can fade away. All three components are essential for making learning not just a fleeting moment, but a lasting journey.
Stay with us, because in our next section we’re going to explore another exciting aspect of memory: the power of emotion and narrative in learning. Until then, think about the library of your mind and how every experience is a book waiting to be written and remembered.
The Power of Emotion and Narrative in Learning
Welcome back, everyone! In this segment, we’re diving into one of the most fascinating aspects of learning: the power of emotion and narrative. Now, let me ask you a question to set the stage: When you think about the lessons or experiences that have stuck with you the most, do you believe it’s because they were delivered as dry, factual information or because they were wrapped in a compelling, emotionally charged story? Keep that question in your mind as we journey through the incredible ways our emotions and narratives shape our memories.
Let’s start by picturing this: imagine you’re sitting in a classroom, and the teacher is reciting a list of historical dates. It might be important, but unless something grabs your attention, it’s all just a blur. Now, contrast that with a moment when you heard a story about a brave individual who overcame tremendous odds, and suddenly, those dates and events become alive. That’s the magic of emotion in learning—it’s like adding color to a black-and-white photo.
Our brain is wired in such a way that emotions play a critical role in how memories are formed. Deep in our brain, we have the amygdala—the part that processes emotions like fear, joy, and excitement. Right next door is the hippocampus, the key player in forming and storing memories. When an event triggers a strong emotional response, the amygdala sends signals to the hippocampus, making sure that the memory of that event is encoded more robustly. Essentially, our brains treat emotionally charged experiences as high-priority, filing them away with extra care.
Let’s put this into perspective with a story. I remember a time during my college years when I attended a guest lecture by a war veteran. Instead of just delivering facts about historical battles, he recounted his own harrowing experiences on the front lines. He described the deafening sounds of explosions, the fear that gripped him as he made split-second decisions, and the profound loss he felt when he lost a close comrade. His narrative wasn’t just about history; it was about life, sacrifice, and the raw emotion of survival. Even now, years later, that lecture is etched vividly in my memory—not because I memorized dates and figures, but because I felt every word he said.
This isn’t a coincidence. Research shows that when learning is paired with emotional experiences, our ability to recall information is significantly enhanced. The brain doesn’t treat all information equally; it prioritizes what matters most. Emotion acts like a spotlight, illuminating certain details and pushing them into long-term storage. It’s the reason you might vividly remember the details of a thrilling movie or a moving piece of music long after the experience has faded from your daily consciousness.
Now, let’s make this interactive. I invite you to pause for a moment and recall a personal memory that has stayed with you over the years. It could be something as simple as a childhood birthday party, or as profound as a moment of achievement or loss. Ask yourself: What made that memory so enduring? Was it the laughter, the tears, or the sheer excitement of the moment? Perhaps it was a combination of all these emotions. Feel free to share your thoughts with a friend, or jot them down later. Reflecting on these experiences helps you understand the immense power of emotion in your own life.
Moving on, let’s talk about narrative—the art of storytelling. Humans have been telling stories for thousands of years. Before we had books, movies, or even formal education, our ancestors passed down knowledge through stories. Why? Because stories are inherently memorable. They engage multiple parts of our brain simultaneously: they evoke emotions, create vivid images, and often connect to our personal experiences. When information is presented as a story, it is not only easier to understand but also far more engaging and lasting.
Consider a historical example: The legend of the Trojan War. While historians debate the factual accuracy of the events, the story itself has captivated minds for centuries. It’s not just a collection of dates and battles; it’s a narrative filled with heroism, betrayal, love, and tragedy. The characters become almost real—heroes and villains you can relate to. And because the narrative is so rich, it transcends time. That’s the power of storytelling in action: it transforms simple facts into memorable experiences that resonate deeply within us.
Now, you might be wondering, “How exactly does a narrative enhance our memory?” Well, when we hear a story, our brains are busy at work. We don’t just passively listen; we actively construct mental images and emotions. This process involves multiple brain regions working together. The sensory details in a story—the sounds, the sights, the emotions—are all encoded along with the core information. Later, when we try to recall the story, we have multiple “retrieval cues” that help us access the memory. Each cue, be it a particular emotion or a vivid image, serves as a reminder of the entire narrative.
Here’s a little exercise for you. Think about a time when you learned something new—maybe a scientific concept or a historical event. Now, try to recall the lesson as a story. Did you imagine characters or a setting? Did you feel a particular emotion? Chances are, when you reframe that information as a narrative, it becomes easier to remember. This isn’t just a trick for students; it’s a natural way our brains process information. In fact, many of the most effective teaching methods today incorporate storytelling because it mirrors the way we evolved to learn.
Before we circle back to our initial question, let’s address another interesting angle: the interplay between emotion and narrative isn’t just a one-way street. While emotions enhance the memorability of narratives, the narrative context can also shape our emotional response. For example, if you’re told a story in a monotone voice, even if the content is inherently emotional, the impact might be lost. But if the storyteller uses vivid language, pauses for dramatic effect, and infuses the narrative with genuine feeling, the emotional resonance is amplified. This dynamic interaction means that both emotion and narrative are critical partners in the learning process.
I’d love for you to experiment with this. Next time you’re trying to remember something important—be it a new vocabulary word, a historical fact, or even a professional skill—try to create a little story around it. Imagine a scenario where that piece of information plays a crucial role. By doing so, you’re not only engaging your brain’s natural love for stories but also creating emotional hooks that will help you recall the information later.
Now, let’s circle back to that question I posed at the beginning of this section: When you think about the lessons or experiences that have stuck with you the most, is it because they were delivered as dry, factual information, or because they were embedded in a compelling, emotional narrative? If you’re like most people, you probably realize that the memories that have truly stuck with you are those that touched your heart, that painted a vivid picture, and that resonated with your emotions. The answer is clear: our brains are wired to remember stories that evoke emotion, not lists of isolated facts.
In summary, the power of emotion and narrative in learning lies in their ability to transform mundane information into dynamic, memorable experiences. Emotions act as a highlighter for our brains, marking certain details as important, while narratives provide a framework that makes the information engaging and easy to recall. When these two elements combine, they create a potent recipe for lasting memory. So next time you’re studying or trying to learn something new, remember to infuse it with a little emotion and a dash of storytelling—it just might make all the difference.
Thank you for joining me on this exploration of how our feelings and stories shape the way we learn. Remember that little question: Do you think it’s the emotional context or the repetition of facts that really cements a memory? I hope by now you can see that while repetition has its place, nothing beats the power of a well-told story that resonates with your emotions. So go ahead and harness that power in your learning journey, and see just how memorable your lessons can become.
Memory Techniques & Strategies
Welcome back, everyone! In this segment, we’re shifting gears to dive into some practical memory techniques and strategies that can transform the way you learn and retain information. Before we get started, I want to pose a question to you: out of all the techniques we’re about to explore—mnemonics, the method of loci (or memory palace), and spaced repetition—which one do you think is the most effective for boosting memory retention? Hold that thought as we explore each method in depth, and we’ll circle back to answer it by the end of this section.
Let’s begin with mnemonic devices. You’ve probably heard the term “mnemonic” before—it’s simply a fancy word for a memory aid, a tool that helps you recall larger pieces of information through a simple, often playful mechanism. One classic example is the acronym “HOMES” used to remember the names of the Great Lakes: Huron, Ontario, Michigan, Erie, and Superior. This technique works because it condenses complex or long lists into a single, easily remembered word. Now, take a moment: think about a list of items you need to remember—perhaps a grocery list or a set of vocabulary words. Could you create a similar acronym to help you remember them? Try it out mentally right now; the process of creating an acronym itself reinforces the memory.
Moving on, let’s talk about another mnemonic strategy that relies on vivid imagery. This technique is all about linking the information you want to remember with a visual image. For example, if you need to remember the word “cantaloupe,” you might imagine a giant, cantaloupe-shaped hat perched atop your head. The sillier or more exaggerated the image, the more likely it is to stick in your mind. This method plays into the fact that our brains are exceptionally good at recalling visual details. As an interactive exercise, think of a word you find challenging to remember and try to create a vivid, humorous image in your mind associated with it. Even if the image seems a bit out there, that’s exactly what makes it memorable!
Now, let’s explore one of the most celebrated techniques in the world of memory improvement—the method of loci, also known as the memory palace technique. This method leverages our innate ability to remember spatial information. Here’s how it works: you visualize a familiar place, like your home, and then “place” the items you want to remember along a specific route within that space. For instance, if you’re trying to remember a list of five vocabulary words, you might imagine placing each word in a different room or at a distinct landmark along the hallway. Later, when you need to recall the words, you mentally walk through your memory palace, and the items appear in the order you set them.
Let’s make this interactive right now. Close your eyes if you can, and picture the layout of your home. Now, imagine you have to remember the following five words: “serendipity,” “eloquent,” “resilient,” “meticulous,” and “vibrant.” Visualize placing “serendipity” at your front door, “eloquent” in your living room, “resilient” in the kitchen, “meticulous” in the study, and “vibrant” in your bedroom. As you walk through your home in your mind, notice how each word is anchored to a specific location. This exercise not only makes the information easier to recall but also turns the process of learning into a creative, engaging experience.
Next up is spaced repetition, a strategy that takes advantage of the way our brains naturally consolidate memories over time. Spaced repetition involves reviewing information at gradually increasing intervals. Think of it like watering a plant: you don’t dump a gallon of water on it all at once; you water it regularly, allowing it to absorb the moisture over time. There are many digital tools available, such as flashcard apps, that use this method. By consistently reviewing the information just as you’re about to forget it, you reinforce the memory and make it stick.
Imagine you’re using an app like Anki or Quizlet. When you first learn a new concept, the app will prompt you to review it soon after. Each time you recall the information correctly, the interval before the next review grows longer. This method optimizes your study time by focusing on the items that need reinforcement, making your learning process both efficient and effective. As you listen, consider the last time you crammed for an exam—how different might your performance have been if you’d spaced out your study sessions over several days or weeks instead?
We also have another useful strategy called active recall, which is closely related to spaced repetition. Active recall involves testing yourself on the information you’re trying to learn rather than passively reviewing it. Instead of re-reading your notes, you might cover them up and try to recite the key points from memory. This act of retrieval strengthens your memory and highlights areas that need further review. For an interactive tip, next time you study, try turning your notes into a series of questions and then quiz yourself. It might feel a bit challenging at first, but you’ll be surprised at how much more effectively you retain the information.
Another technique worth mentioning is chunking, which involves breaking down large amounts of information into smaller, manageable “chunks.” This method is particularly useful when you’re dealing with complex data or long sequences of numbers. For example, instead of trying to remember a long string of digits like 1-9-4-5-2-0-2-5 all at once, you might break it down into two chunks: 1945 and 2025. Our brains naturally find it easier to process and remember smaller groups of information rather than one overwhelming block.
Now, let’s revisit the question I posed at the beginning of this section: Out of the memory techniques we’ve discussed—mnemonic devices, visualization, the method of loci, spaced repetition, and active recall—which one do you think is the most effective for boosting memory retention? I want you to think about that as we wrap up this discussion.
Each technique we’ve talked about offers its own unique advantages. Mnemonics and vivid imagery turn abstract information into concrete, memorable pictures. The method of loci taps into our powerful spatial memory by associating data with familiar locations. Spaced repetition and active recall, on the other hand, are rooted in the science of how our brains consolidate and retrieve information over time. And then there’s chunking, which simplifies complex information into bite-sized, digestible pieces.
So, which technique is the most effective? The answer isn’t cut-and-dried—it really depends on the individual and the type of information you’re trying to learn. However, many experts in the field of memory improvement argue that the method of loci, or memory palace technique, stands out as particularly potent. Why? Because it combines several cognitive strengths: spatial memory, visualization, and association. By anchoring information to physical locations that you know intimately, you’re creating a network of cues that can trigger your memory with remarkable precision. That said, the best approach is often a blend of several techniques. For example, you might use mnemonics to simplify the information, then embed that information into a memory palace, and finally reinforce it with spaced repetition. This multi-faceted strategy ensures that you’re engaging your brain in various ways, making the memory even more resilient.
Before we wrap up, I’d like to invite you to experiment with these techniques in your own study routines. Next time you’re learning something new—be it a set of vocabulary words, historical facts, or even a complex theory—try incorporating one or more of these methods. Create a mnemonic, build a memory palace, or set up a spaced repetition schedule. Notice how your ability to recall information improves and how much more engaging the learning process becomes.
As we circle back to our opening question, think about which technique resonates most with you. If you’re someone who thrives on visual and spatial cues, the method of loci might be your go-to tool. If you find that humor and clever wordplay help you remember details, mnemonics might be more your style. And if you prefer a systematic, structured approach, then spaced repetition combined with active recall could be the key to unlocking your learning potential.
Ultimately, the most effective memory technique is the one that fits your personal learning style. There’s no one-size-fits-all answer—each strategy has its own strengths, and the best results often come from using them in tandem.
Thank you for joining me on this deep dive into memory techniques and strategies. I hope you feel inspired to try out these methods and experience firsthand the transformative power they can have on your learning journey. Remember, your brain is capable of amazing things, and sometimes all it takes is a little creativity and practice to unlock its full potential. Now, take a moment to reflect: Which memory technique will you experiment with first? I’d love for you to share your thoughts or even your own personal strategies as you continue on your path to mastering memory and learning.
Practical Application & Case Study – From Classroom to Career
Welcome back, everyone! In this section, we’re going to shift from theory to practice by exploring how memory techniques and learning retention strategies can make a real, tangible difference in both academic and professional settings. Before we dive into a compelling case study, I’d like to ask you a question: Have you ever wondered which specific memory strategy truly makes the biggest impact when transitioning from classroom learning to a thriving career? Stick with me as we explore a real-life story that not only answers this question but also provides practical insights you can apply to your own life.
Let’s begin with a story about Alex, a young professional who once struggled to keep up with the ever-increasing demands of college. Like many students, Alex found that no matter how hard he studied, some lessons just wouldn’t stick. Important concepts would fade away, and exam stress often left him frustrated. One day, after a particularly challenging exam, Alex decided that the traditional methods of rote memorization weren’t working for him. Determined to find a better approach, he began exploring different memory techniques—everything from mnemonics and spaced repetition to the method of loci.
At first, Alex was skeptical. How could a simple change in study habits really make such a big difference? He experimented with mnemonic devices by creating quirky acronyms and vivid visual images to remember complex theories in physics. For instance, to recall the laws of motion, he devised a little story about a clumsy robot named “Newton” who kept bumping into obstacles. This method not only brought a smile to his face but also made the abstract laws more relatable and easier to recall.
Next, Alex delved into the method of loci, building his very own memory palace. He started by mapping out his childhood home in his mind, assigning different rooms and familiar spots to various pieces of information. For example, he placed the steps of a complicated math formula along the hallway, associating each step with a distinct piece of furniture. This spatial organization helped him create strong, interconnected memory cues that were hard to forget.
But the breakthrough really came when Alex began integrating spaced repetition into his study routine. Instead of cramming all night before exams, he scheduled regular review sessions that gradually increased in interval as he mastered the content. With the help of a simple flashcard app, he was reminded to revisit topics just as they were about to slip from his memory. This systematic approach turned his study sessions into a rhythm of continuous reinforcement, leading to a noticeable improvement in his retention and understanding.
Now, you might be thinking, “That sounds great for a student, but how does this translate into a professional setting?” Well, here’s where Alex’s journey takes an exciting turn. After college, Alex landed a job at a competitive tech firm where keeping up with rapid advancements in technology was part of the daily grind. In this new environment, the ability to quickly learn and retain complex information became even more critical. Rather than relying solely on formal training sessions, Alex applied the same memory techniques that had helped him during his studies.
In meetings, instead of taking endless notes that he knew he’d later forget, Alex used mental imagery and mnemonic devices to capture key points. He visualized the structure of software projects as physical buildings, each component represented by a unique landmark in his mind. This not only made it easier for him to recall details during discussions but also allowed him to contribute creative solutions by drawing unexpected connections between different ideas.
One particular project required Alex to master a new programming language in just a few weeks. The pressure was intense, and the learning curve was steep. Recalling the success he had with his memory palace technique in college, he constructed a new mental map, this time using his favorite park as the backdrop. Each section of the park—the playground, the pond, the flower garden—represented different syntax rules and coding structures. By revisiting this mental map daily, he reinforced the new language’s concepts in a manner that was both structured and enjoyable.
What’s even more fascinating is how these techniques not only improved Alex’s professional performance but also boosted his overall confidence. In one instance, during a critical presentation, he was able to recall complex data and analysis without relying on slides or notes. His colleagues were impressed by how seamlessly he integrated memory techniques into his workflow, and his manager later remarked that Alex’s ability to retain and apply new information was a key factor in the team’s success.
Let’s pause here for a moment and invite you to participate. Think about your own learning experiences—whether you’re a student, a professional, or someone who’s just passionate about acquiring new knowledge. Have you ever tried using any memory techniques, or do you rely mostly on traditional study methods? Perhaps you’ve found that certain techniques work better for specific types of information. Take a moment to consider: what might your memory palace look like, or what mnemonic device could help you remember your next big project or presentation? Reflecting on these questions is the first step toward transforming your learning process.
Returning to our story, Alex’s journey demonstrates a powerful truth: the strategies that work in the classroom are not confined there. They are versatile tools that, when adapted properly, can serve you well in the dynamic world of professional life. The transition from academic success to career success often hinges on one’s ability to continuously learn and adapt. By using memory techniques like mnemonics, the method of loci, and spaced repetition, Alex not only mastered challenging subjects but also built a skill set that kept him ahead of the curve in his career.
Now, let’s circle back to the question we started with: Which memory strategy makes the biggest impact when transitioning from classroom to career? Throughout Alex’s journey, he experimented with several techniques, but the one that consistently stood out was the method of loci—his memory palace. This approach uniquely combined spatial memory with vivid visualization, allowing him to anchor complex information to familiar environments. While mnemonics and spaced repetition were incredibly useful in reinforcing details, the method of loci provided a robust framework that transformed abstract concepts into concrete, memorable images. It was this technique that not only helped him excel academically but also gave him the confidence to handle high-pressure situations at work.
So, to answer our initial question: The method of loci—or memory palace technique—proved to be the most impactful for Alex when moving from the classroom to his career. It harnessed the power of visualization and spatial organization to create lasting memory cues that were easily accessible when needed. However, it’s important to remember that the best approach often involves a combination of strategies. Experiment with different techniques and see which ones resonate most with your personal learning style.
As we wrap up this section, I encourage you to take a page from Alex’s book. Try integrating these memory techniques into your daily routine, whether you’re preparing for an exam, tackling a new project at work, or simply trying to retain more from your everyday experiences. The tools are there for you—mnemonics, memory palaces, spaced repetition, and active recall—and they have the potential to transform the way you learn, retain, and apply information in all areas of life.
I hope Alex’s story inspires you to experiment with these techniques and discover your own path to effective learning. Now, think back to our opening question and the answer we’ve revealed: For transitioning from classroom learning to professional success, the memory palace stands out as a powerful tool. What technique will you experiment with first in your own journey toward better memory and improved learning retention? I’d love for you to reflect on this and even share your experiences with friends or colleagues. Let’s continue this journey together, one memorable step at a time.
Practical Application & Case Study – Digital Tools & the Future of Learning
Welcome back, everyone! In this segment, we’re exploring how digital tools are revolutionizing the way we learn and retain information. Today’s focus is on practical applications and a real-life case study that demonstrates how technology is bridging the gap between ancient memory techniques and modern learning. But before we dive in, I have a question for you: Which digital tool do you think is transforming our learning experience the most—adaptive flashcard apps, immersive virtual reality platforms, or AI-driven tutoring systems? Keep that question in mind as we journey through this exciting landscape, and we’ll circle back to it at the end.
Let’s start by looking at how traditional memory techniques, like spaced repetition and the method of loci, have found new life in the digital age. Think back to when you used flashcards in school—maybe you scribbled words or concepts on index cards and shuffled through them repeatedly. Now, imagine that process amplified by technology. Digital flashcard apps like Anki and Quizlet have taken the concept of spaced repetition and refined it with precision. These apps use algorithms to schedule reviews at just the right time, ensuring that information moves from short-term to long-term memory in the most efficient way possible. They do this by tracking your performance and adapting the intervals between reviews, making sure you’re revisiting concepts right when you’re about to forget them.
If you have a smartphone or a computer nearby, take a quick moment to open your preferred flashcard app or recall one you’ve used before. Notice how it structures your review sessions. This isn’t just about convenience—it’s a scientifically backed approach to maximize your retention, all thanks to digital innovation.
Beyond flashcards, the digital world has introduced immersive tools that bring memory techniques to life. Picture this: Instead of merely visualizing a memory palace in your mind, you can now build one in a virtual environment. Virtual reality (VR) platforms are beginning to offer experiences where you can construct, explore, and interact with your own memory palaces in a fully three-dimensional space. Imagine walking through a virtual museum where each exhibit represents a piece of the information you’re trying to learn. Not only does this make learning more engaging, but it also leverages spatial memory in a way that traditional studying simply can’t match.
Now, let’s talk about AI-driven tutoring systems, which are perhaps the most futuristic development in learning today. These systems use artificial intelligence to personalize your learning experience. For example, an AI tutor might analyze your study patterns, pinpoint areas where you struggle, and then adapt the material in real time to help you understand those concepts better. This level of customization is like having a personal coach who knows your strengths and weaknesses and adjusts the lessons accordingly. Whether you’re learning a new language or mastering a complex subject, AI tutors provide immediate feedback and suggest targeted exercises that reinforce what you’ve learned.
I want you to consider your own learning experiences here. Have you ever felt that a one-size-fits-all approach just didn’t work for you? Perhaps you found yourself either bored by content that was too easy or overwhelmed by material that was too advanced. Digital tools, particularly those powered by AI, are addressing these challenges head-on by creating adaptive learning paths that respond to your pace and style. This is the future of education—one where technology ensures that every learner receives exactly what they need to succeed.
Let’s delve into a real-life case study that ties all these innovations together. Meet Jordan, a dedicated professional who needed to upskill quickly for a career transition into data science. Jordan had a busy schedule and couldn’t afford the luxury of inefficient learning methods. Initially, Jordan tried traditional textbooks and online courses, but the pace was too slow and retention was minimal. That’s when Jordan turned to a suite of digital tools designed to supercharge learning retention.
First, Jordan adopted an adaptive flashcard app that used spaced repetition to drill core concepts in statistics and programming. Every day, Jordan spent just 15 minutes reviewing flashcards, and the app’s algorithm ensured that each concept was revisited at the optimal time for maximum retention. Soon, Jordan noticed a dramatic improvement—not only in recalling definitions and formulas but also in understanding how these pieces fit into larger concepts.
Encouraged by this success, Jordan then experimented with a VR-based learning platform. In this virtual environment, complex data structures and algorithms were represented as interactive, 3D objects. Instead of struggling with abstract diagrams on a page, Jordan could manipulate virtual models to see how data flowed through systems in real time. This immersive experience made the learning process not only more enjoyable but also more intuitive. Concepts that had once seemed impenetrable began to click, as Jordan’s mind linked the physical manipulation of objects to the abstract ideas they represented.
Finally, to tie it all together, Jordan used an AI-powered tutoring system that provided personalized feedback on practice projects. This system tracked Jordan’s progress, identified recurring mistakes, and suggested targeted exercises. The AI even simulated real-world scenarios that required applying learned concepts to solve practical problems. Over time, Jordan’s confidence grew, and so did the mastery of the material. In a matter of months, Jordan not only landed a job in data science but also became known among peers for a deep, intuitive understanding of complex subjects—a transformation that was powered by the synergy of digital tools and proven memory techniques.
I invite you to reflect on your own journey with digital learning tools. Have you ever used an app, VR environment, or AI tutor that made a real difference in your understanding of a subject? Think about the features that stood out—was it the personalized feedback, the engaging visuals, or the structured repetition that made the impact? Jot down a few thoughts or share them with a friend. Recognizing these moments can help you pinpoint which tools might work best for your own learning style.
Now, let’s circle back to the question I posed at the beginning of this section: Which digital tool do you think is transforming our learning experience the most? After exploring the realm of adaptive flashcards, immersive VR platforms, and AI-driven tutoring systems, it becomes clear that while each tool has its strengths, the real game-changer is the integration of these technologies into a seamless, adaptive learning ecosystem. For many learners, the adaptive flashcard apps stand out because they directly implement the science of spaced repetition—a method proven to enhance memory retention significantly. However, the immersive experiences offered by VR and the personalized coaching of AI tutors are rapidly catching up, promising to further tailor the learning process to individual needs.
So, if I were to answer the question directly, I’d say that right now, adaptive flashcard apps are the most accessible and effective tool for boosting memory retention, largely because they embody the core principles of cognitive science in a user-friendly format. That said, the future is bright and evolving: as VR and AI technologies mature, we’re likely to see even more powerful integrations that will redefine how we learn. The digital tools of tomorrow will likely combine the best aspects of each method, offering a holistic approach that not only makes learning more efficient but also more engaging and personalized.
To wrap up this section, remember that technology is not replacing the fundamental principles of memory and learning; it’s enhancing them. Tools like adaptive flashcards, VR environments, and AI tutors are extensions of time-tested techniques like spaced repetition, visualization, and active recall. They provide the scaffolding needed to support your learning journey in a rapidly changing world.
Thank you for joining me as we explored how digital innovations are shaping the future of learning. I hope Jordan’s story and the examples we discussed inspire you to experiment with these tools and discover which ones resonate with your personal learning style.
Let’s Learn Vocabulary in Context
Welcome to our vocabulary guessing game! We’ll be taking 10 words or phrases straight from our discussions in this episode. For each one, we’ll give you three clues before revealing the answer. Remember, your mission is to guess the word or phrase before we reveal it. Ready? Let’s begin!
1. Mystery Word #1
Clue 1: Meaning
This concept is all about transforming new information into a format that your brain can store. Think of it as the initial “writing” phase, where your mind takes something from the outside world and prepares it to be filed away. Without this step, it’s nearly impossible to remember anything later on. You might compare it to saving a new document on your computer—if you never save it, you’ll lose it when you shut down!
Clue 2: Context in Our Episode
We talked about this process when explaining how our brains take in everything from words to experiences and turn them into lasting mental impressions. We mentioned that if you don’t pay attention or don’t connect the new information with something meaningful, this process doesn’t happen efficiently.
Clue 3: First Letter
This word starts with the letter E.
Take a moment to guess!
Reveal
The word is Encoding! Encoding is crucial because it determines whether something we experience actually becomes a memory. If you want to encode more effectively, you can use techniques like creating vivid mental images or connecting new ideas to emotions or previous knowledge.
2. Mystery Word #2
Clue 1: Meaning
This is what happens when you’re digging through your mental “library” and pulling up the information you’ve stored. Sometimes, this process is easy—like remembering your home address—and sometimes it’s tricky—like recalling the name of the actor in that one movie you saw years ago. It’s essentially the act of “getting things back out” after you’ve put them away for safekeeping.
Clue 2: Context in Our Episode
We highlighted this concept when discussing how our minds use “cues” like emotions or environmental reminders. These cues trigger the memory you want, making the act of recalling information simpler or faster.
Clue 3: First Letter
This word starts with the letter R.
Take a moment to guess!
Reveal
The word is Retrieval! Retrieval is vital because it’s the final step in using your memory. You could have stored plenty of information, but if you can’t retrieve it at the right time, it’s not very helpful. That’s why techniques like spaced repetition and active recall are so powerful—they strengthen your retrieval pathways.
3. Mystery Phrase #3
Clue 1: Meaning
This phrase describes an ancient technique where you imagine a familiar place, such as your home, and place the things you need to remember in specific spots around that place. Later, when you mentally “walk” through it, you can find each item in its designated location. It’s as if you’re building a mental map where each point triggers your memory.
Clue 2: Context in Our Episode
We used this term when we explored how pairing spatial awareness with vivid visualizations can make information stick. We shared stories about placing vocabulary words or steps of a process in different rooms to make them more memorable.
Clue 3: First Letter
This phrase starts with the letter M.
Take a moment to guess!
Reveal
The phrase is Memory Palace (also known as the Method of Loci)! This approach is particularly powerful for memorizing lists or sequences because it leverages our natural ability to remember places. It’s fun, creative, and incredibly effective once you get the hang of it.
4. Mystery Word #4
Clue 1: Meaning
This term refers to revisiting information over gradually increasing intervals, rather than trying to cram it all in at once. It’s like periodically watering a plant so it stays healthy over time, instead of drenching it once and letting it wither. By reviewing material just as you’re about to forget it, you give your brain a chance to reinforce the memory.
Clue 2: Context in Our Episode
We explained how apps and programs use this concept to prompt you to study words or concepts at exactly the right time. This method helps move knowledge from short-term to long-term memory.
Clue 3: First Letter
This word starts with S.
Take a moment to guess!
Reveal
The word is Spaced Repetition! If you’ve used flashcard apps like Anki or Quizlet, you’ve likely experienced spaced repetition in action. It optimizes your study schedule to make learning more efficient.
5. Mystery Word #5
Clue 1: Meaning
Imagine you have to remember a list of random facts. This concept involves using a variety of creative tricks—like acronyms, silly sentences, or songs—to help you recall these facts. It can turn an otherwise boring list into something playful and unforgettable.
Clue 2: Context in Our Episode
We talked about how some people remember the order of planets with a funny sentence or how you might recall complicated scientific terms using clever word associations.
Clue 3: First Letter
This word starts with M.
Take a moment to guess!
Reveal
The word is Mnemonics! Mnemonic devices can be as simple as acronyms or as elaborate as entire stories. They’re excellent tools for tackling everything from vocabulary lists to historical dates.
6. Mystery Word #6
Clue 1: Meaning
This is the part of your brain responsible for processing emotions—particularly fear and pleasure—and it can strongly influence which memories stick. It’s like the emotional gatekeeper that says, “Hey, this is important; pay attention!” or “Meh, not a big deal.”
Clue 2: Context in Our Episode
We brought up this brain structure when talking about how strong emotions can make memories more vivid and long-lasting, often influencing the learning process in powerful ways.
Clue 3: First Letter
This word starts with A.
Take a moment to guess!
Reveal
The word is Amygdala! The amygdala sends signals to other parts of the brain, particularly the hippocampus, telling it to store the emotionally charged events more securely. That’s why emotionally significant moments often become our strongest memories.
7. Mystery Word #7
Clue 1: Meaning
Picture a tiny seahorse-shaped structure in your brain (yes, really!), tasked with forming and organizing new memories. It’s a superstar for transferring information from short-term to long-term storage. Without this little powerhouse, learning new things becomes much more difficult.
Clue 2: Context in Our Episode
We mentioned this when discussing how the brain physically files away memories, highlighting its pivotal role in both academic and real-world learning.
Clue 3: First Letter
This word starts with H.
Take a moment to guess!
Reveal
The word is Hippocampus! Fun fact: it’s called “hippocampus” because it resembles a seahorse in shape. If you ever come across memory research, you’ll probably hear a lot about how vital this structure is to learning.
8. Mystery Word #8
Clue 1: Meaning
This learning strategy involves testing yourself on the material rather than simply re-reading it or passively reviewing notes. By actively trying to recall the information, you strengthen the neural pathways that help you remember it later. Think of it like flexing your brain’s “memory muscle.”
Clue 2: Context in Our Episode
We mentioned this when explaining how quizzes, flashcards, and even self-made questions can boost memory by forcing you to retrieve information, rather than just recognizing it on a page.
Clue 3: First Letter
This phrase starts with A (two words, both starting with A and R).
Take a moment to guess!
Reveal
The phrase is Active Recall! Active recall is more challenging than passive reading, but it’s one of the best ways to truly lock information into your long-term memory. It’s like working out—you only get stronger if you actually lift the weights.
9. Mystery Phrase #9
Clue 1: Meaning
Think of this as your mental “sticky note.” It’s the part of your memory system that holds information temporarily, like a phone number you repeat to yourself until you can dial it. It’s active, limited, and crucial for day-to-day tasks that involve holding a few pieces of information in your mind at once.
Clue 2: Context in Our Episode
We brought up this concept when discussing how you juggle new facts or instructions, highlighting that if you overload this system, you’re more likely to lose track of information quickly.
Clue 3: First Letter
This phrase starts with W (two words, W and M).
Take a moment to guess!
Reveal
The phrase is Working Memory! It’s the short-term mental workspace where you manipulate information before deciding whether it’s important enough to store long-term or discard. Strengthening your working memory can improve everything from math skills to language learning.
That’s it for our vocabulary guessing game! We hope you enjoyed testing your knowledge of these key words and phrases from our episode. Remember, the more you understand these terms and use them in context, the stronger they’ll become in your memory. Feel free to revisit this section anytime to brush up on the vocabulary and concepts we’ve discussed. Keep learning, stay curious, and get ready for the next part of our show!
Let’s Discuss & Write
Discussion Questions
- The Emotional Edge
How much do you think emotions influence your ability to remember something? Can you recall a time when an emotional response (happy, sad, or even frightened) helped you remember a specific event or piece of information more clearly?- Feel free to share details about what made that memory so powerful, and whether you think you can recreate that emotional “spark” for future learning.
- Storytelling as a Superpower
We’ve talked about how narratives and stories can make memories last. Do you have a favorite story or anecdote that cemented a piece of knowledge in your mind?- Share a story that stuck with you for years—maybe it’s a cultural myth, a family tale, or a funny personal experience. Ask yourself: Why do you think it stayed so vivid in your memory?
- Digital Tools in Your Life
What digital tools—if any—have you used to improve your learning or memory retention? Have they worked as well as you hoped, or are there areas where “old-school” methods (like handwritten notes) still reign supreme for you?- If you’ve found a tool that really makes a difference (like a certain app or website), let everyone know about it. Alternatively, share if you have mixed feelings about relying on technology for learning.
- Applying Memory Techniques to Real Life
Which technique from the episode—mnemonics, memory palaces, spaced repetition, or something else—would you be most interested in trying? Why do you feel it fits your learning style?- Let us know if you plan to experiment with these techniques, and consider describing how you might adapt one for a specific task or project in your daily routine.
- Balancing Fun and Focus
Some people argue that having fun while learning (through games, storytelling, or interactive challenges) is essential for retention, while others say that rigorous discipline is more effective. Where do you stand on this spectrum?- Don’t hesitate to bring in personal anecdotes: share whether structured, serious study sessions work best for you, or if you learn faster when it feels more like play.
Writing Prompt
Prompt:
Write a short personal essay (300–500 words) about a learning breakthrough you’ve experienced. Focus on how you overcame a particular challenge using a memory strategy—intentionally or by accident—and what that taught you about your own learning style.
Directions & Tips:
- Set the Scene: Start by describing the moment or situation where you realized you were stuck. Were you prepping for an exam, trying to memorize a long list of facts for work, or learning a new language?
- Detail the Technique: Explain the memory strategy you used—or stumbled upon by chance—and how it helped you break through the barrier. Did you come up with a catchy mnemonic? Did you try building a mental palace?
- Reflect on the Outcome: Describe how this technique changed your approach to learning. Did you feel more confident afterward? Did your results on that test or project improve significantly?
- Share Future Plans: Conclude by discussing whether you plan to use this memory strategy again. If so, how might you modify it or combine it with other techniques?
Useful Phrases You Can Include in Your Essay:
- “The turning point came when I realized…”
- “I discovered a simple yet powerful method…”
- “By linking each piece of information to…”
- “I felt a surge of confidence once I…”
- “This experience taught me the value of…”
Feel free to adapt these phrases to match your own writing style, and remember that the goal is to tell your story in a compelling way, making your learning process meaningful and relatable. We can’t wait to read what you come up with!
Outro
Thank you so much for joining us on this deep dive into the science of memory and learning retention! Today, we explored how our brains encode and retrieve information, the power of storytelling and emotion in boosting retention, a host of practical memory techniques, and even how technology and AI can take our learning to the next level. We hope this episode has inspired you to try out new strategies—whether you’re a student aiming for better grades, a professional seeking a competitive edge, or simply a curious mind determined to keep learning throughout life.
We’d love to hear your thoughts and personal experiences. Head over to the comments section at englishpluspodcast.com and share your favorite memory technique or a breakthrough learning moment. If you enjoyed this episode, don’t forget to subscribe or follow, and consider supporting us on Apple Podcasts or Patreon to unlock premium content—including exclusive lessons, extended episodes, and more tools to enhance your English skills and knowledge.
Finally, remember to check our website englishpluspodcast.com every day for fresh content—articles, practice materials, and more exciting topics to help you grow your language and expand your horizons. Thank you again for choosing English Plus Podcast, and as always, keep exploring, stay curious, and we’ll see you in the next episode!







0 Comments