Introduction
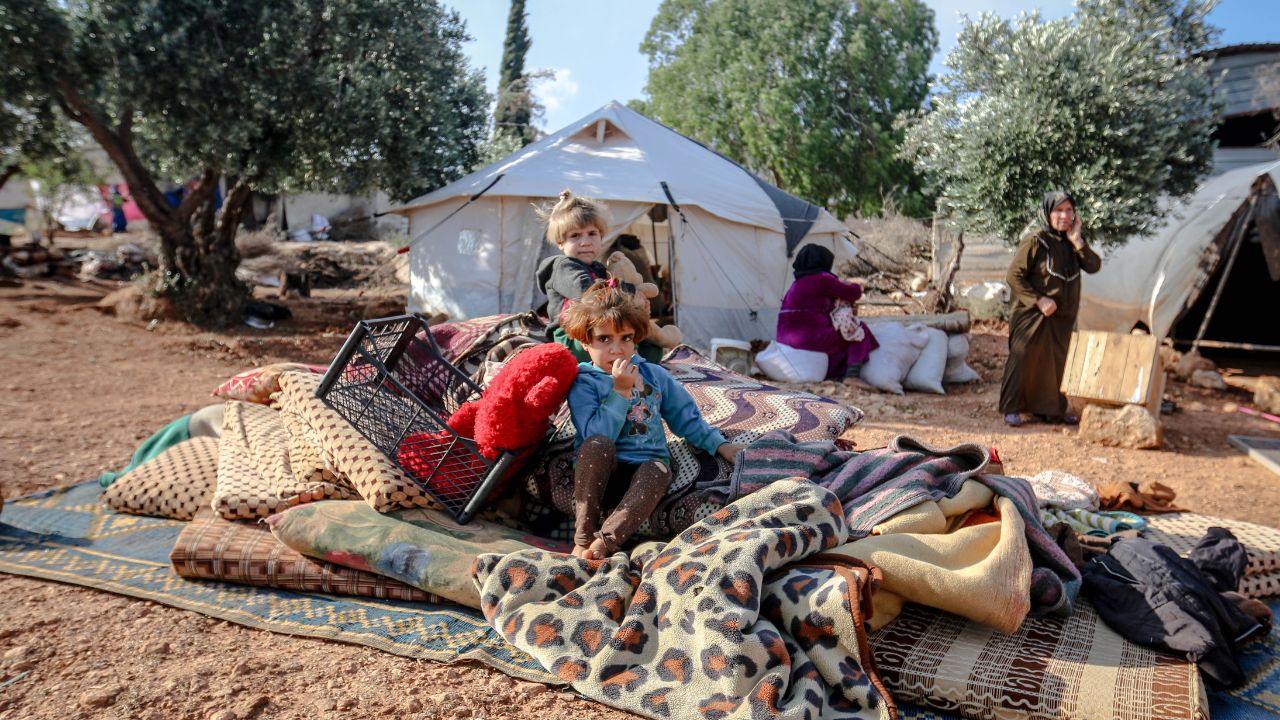
The global refugee crisis has become one of the most pressing and complex humanitarian challenges of our time. With millions of people forcibly displaced from their homes due to conflict, persecution, or natural disasters, the world is witnessing unprecedented levels of human suffering and displacement. This article aims to shed light on the multifaceted nature of the refugee crisis, delving into its causes, consequences, and potential solutions. By exploring these aspects, we hope to foster a greater understanding of the issue and contribute to the ongoing dialogue on how best to address this critical situation.
Causes of the Global Refugee Crisis
Conflict and Persecution
Armed conflicts and political persecution are among the primary factors driving people from their homes. Civil wars, religious or ethnic persecution, and targeted violence against certain groups force individuals to flee in search of safety and protection. Notable examples include the Syrian civil war, the Rohingya crisis in Myanmar, and ongoing conflicts in Afghanistan, South Sudan, and Yemen.
Economic Hardship
Economic factors also play a significant role in the global refugee crisis. In regions with high unemployment, poverty, and lack of opportunity, people often embark on perilous journeys in search of better living conditions and economic prospects. While economic migrants are distinct from refugees, the two groups often face similar challenges and vulnerabilities during their journeys.
Environmental Factors
Natural disasters, climate change, and environmental degradation can lead to population displacement, exacerbating the refugee crisis. For instance, droughts, floods, and hurricanes have left millions homeless and desperate for help. The increasing frequency and severity of such events, fueled by climate change, are expected to contribute to even greater displacement in the coming decades.
Consequences of the Global Refugee Crisis
Humanitarian Impact
The refugee crisis has led to immense human suffering, with millions of people living in precarious situations and facing an uncertain future. Refugees often endure dangerous journeys, with many losing their lives in the process. Those who survive face challenges such as overcrowded camps, inadequate access to healthcare, education, and basic necessities, and a constant struggle for dignity and security.
Sociopolitical Consequences
The influx of refugees and asylum-seekers has put a strain on host countries, especially those with limited resources and infrastructure. This has resulted in rising social tensions, xenophobia, and political instability in some regions. Additionally, the refugee crisis has tested the limits of international law and the global humanitarian system, revealing gaps in the protection and assistance available to displaced persons.
Economic Implications
The global refugee crisis has both positive and negative economic consequences. On the one hand, refugees can contribute to the economies of their host countries by working, paying taxes, and starting businesses. On the other hand, the costs of providing assistance, services, and infrastructure for refugees can be a significant burden, especially for countries already facing economic challenges.
Potential Solutions to the Global Refugee Crisis
Addressing the Root Causes
To effectively tackle the refugee crisis, it is crucial to address the underlying causes of forced displacement. This includes promoting peace, stability, and inclusive governance in conflict-affected areas, as well as investing in sustainable development to alleviate poverty and create opportunities for vulnerable populations. Addressing climate change and supporting disaster resilience is also vital to reduce environmentally-induced displacement.
Strengthening the International Response
Improving the global response to the refugee crisis requires enhanced international cooperation, burden-sharing, and adherence to international legal obligations. This includes providing financial and logistical support to countries hosting large numbers of refugees, ensuring access to asylum procedures, and upholding the principle of non-refoulement, which prohibits the forced return of refugees to countries where they face persecution or danger. Additionally, the international community should invest in the capacity-building of humanitarian organizations and local institutions to ensure effective assistance and protection for displaced persons.
Expanding Legal Pathways for Refugees
To provide refugees with safer and more secure options for seeking protection, governments should expand legal pathways for resettlement, family reunification, and humanitarian visas. By offering alternatives to dangerous and irregular journeys, these measures can help reduce the risks faced by refugees, such as exploitation, trafficking, and death.
Supporting Integration and Self-Reliance
Promoting the successful integration of refugees into host communities is essential for their long-term well-being and self-reliance. This includes providing access to education, healthcare, and employment opportunities, as well as fostering social cohesion through cultural exchange and community engagement programs. Empowering refugees to become active, contributing members of their host societies can benefit both the refugees themselves and the communities that welcome them.
Encouraging Voluntary Repatriation and Local Solutions
When conditions permit, voluntary repatriation—returning refugees to their countries of origin in safety and dignity—can be a sustainable solution to displacement. The international community should support efforts to create the necessary conditions for repatriation, including rebuilding infrastructure, fostering reconciliation, and ensuring the protection of returnees. In situations where repatriation is not feasible, promoting local integration or resettlement to third countries can offer durable solutions for refugees.
Conclusion
The global refugee crisis is a complex and multifaceted issue that demands a comprehensive, collaborative, and compassionate response. By understanding the root causes and consequences of forced displacement, we can work towards developing effective solutions that not only alleviate the suffering of millions of refugees but also address the underlying factors that drive people from their homes.
It is crucial for the international community to come together to support refugees and host countries, uphold international legal obligations, and invest in long-term, sustainable solutions that promote peace, stability, and development. By doing so, we can contribute to building a more just, inclusive, and resilient world that protects the rights and dignity of all individuals, regardless of their nationality or circumstances.
Crossword Puzzle in Context
All the words in the following crossword puzzle are mentioned in the article above.




0 Comments